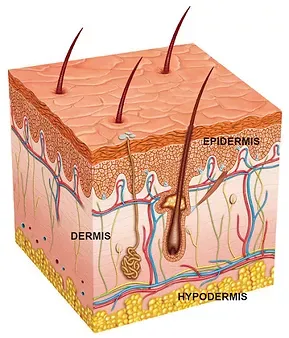
The Skin is divided into two types of tissues. The outer part is called the epidermis and the lower, the dermis. In turn, the epidermis is made of two kinds of layers, a single basal and multiple squamous (suprabasal) layers. There are several types of cells in skin including keratinocytes, melanocytes, sebeocytes, tactile receptor, and immune surveillance cells. They all have different functions, but keratinocytes are the most abundant cells in the epidermis. Keratinocytes have a high concentration of proteins called keratins. Keratins have an important role in the normal function of skin. On the other hand, Melanocytes are less abundant but produce melanin, the brownish pigment that gives skin its color and is responsible for tanning when in the sun.
The epidermis continually renews itself every about every 45 days. It is the job of professional adult stem cells in the basal layer to make more skins cells. An adult stem cell is an immature type of cell that can make more of itself (self-renewal) or become a mature cell (differentiation). There are also stem cells in the hair follicles that activate to renew skin or repair skin when wounded or damaged. The fate of a keratinocyte stem cell is to become a squamous cell, which then dies and is shed off as they become fully mature. This process is call desquamation and can be seen when skin is defoliated. Unlike the mature squamous cells that are transient, the stem cells reside in the epidermis for lifetime. Unfortunately, stem cells can become cancerous after continual exposure to environmental insults like too much UV or toxic chemicals (e.g., arsenics).
Your skin has 3 layers:
One of the most beneficial things that your skin does for you is protect you from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun!
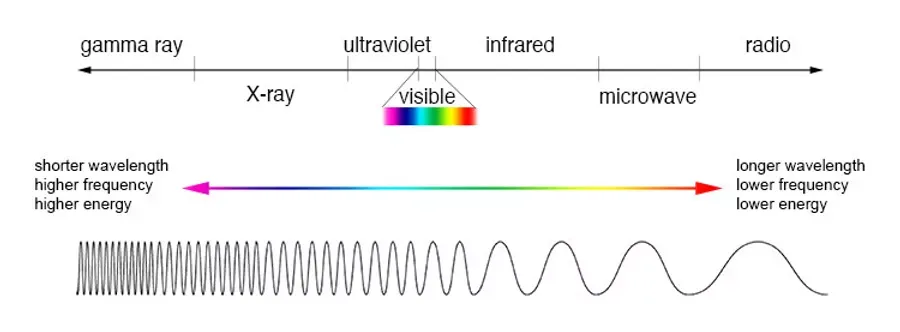
Our sun is a source of energy across the Electromagnetic Spectrum, and its radiation bombards our atmosphere constantly. Electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. The human eye can only detect a small portion of this spectrum called visible light.
UV Radiation
is classified into 3 primary types:
The amount of UV light the skin comes into contact with depends on many factors, such as the time of day, the season, altitude and geographical location. During times of intense UV radiation, for example midday on a hot summer’s day, it is advisable to wear protective clothing and sunscreen when going out doors. Residents of Colorado have the highest UV exposure in the country due to our high elevation, lack of protective atmosphere, +300 days of sunshine every year, and love for the outdoors. Tourists visiting Colorado's ski resorts receive up to 80% additional ultraviolet radiation as it reflects off the snow.
Too much exposure to UV radiation can cause sunburn, premature skin aging, damage to the eyes, a weakened immune system, photoallergic and phototoxic reactions, and even skin cancer. UV rays are able to penetrate the outer skin layers and pass into the deeper layers, where they can damage the DNA in cells. Keratinocyte stem cells and melanocytes with damaged DNA can replicate and, depending on each individual's genetic make-up, become cancerous.
Most skin cancers are a result of exposure to harmful UV in sunlight and man-made sources of UV like indoor tanning beds. Both Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinomas (the most common types of skin cancer) are more likely to be found on sun-exposed parts of the body, and their occurrence is typically related to lifetime exposure to harmful UV. The risk of melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, is also related to sun exposure, although the link is not as strong.